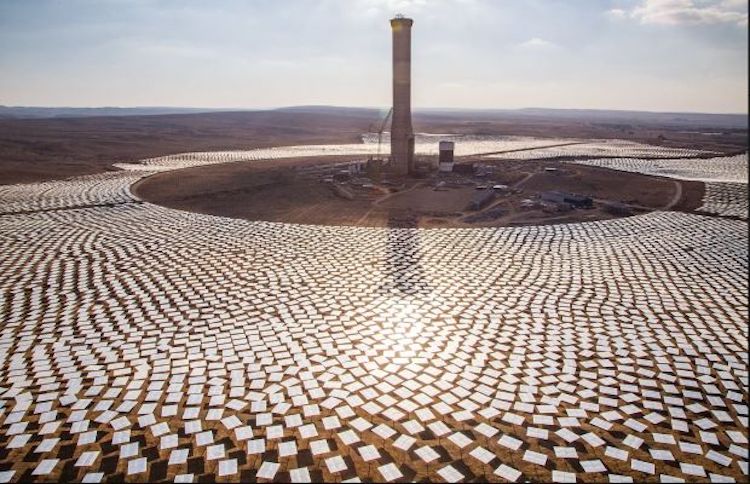
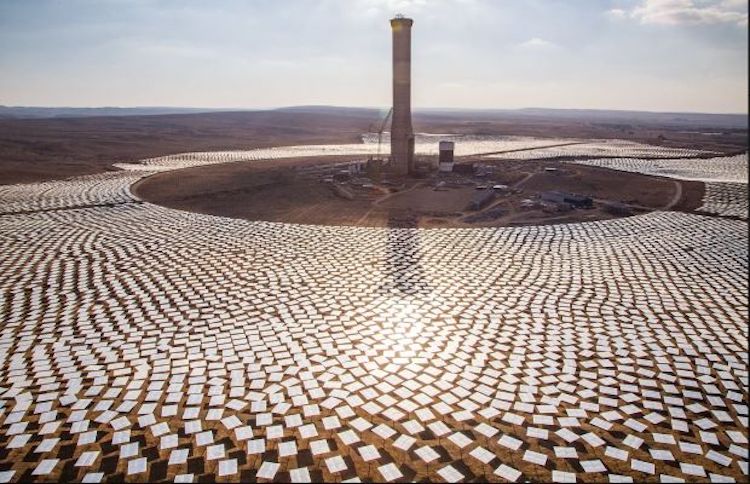
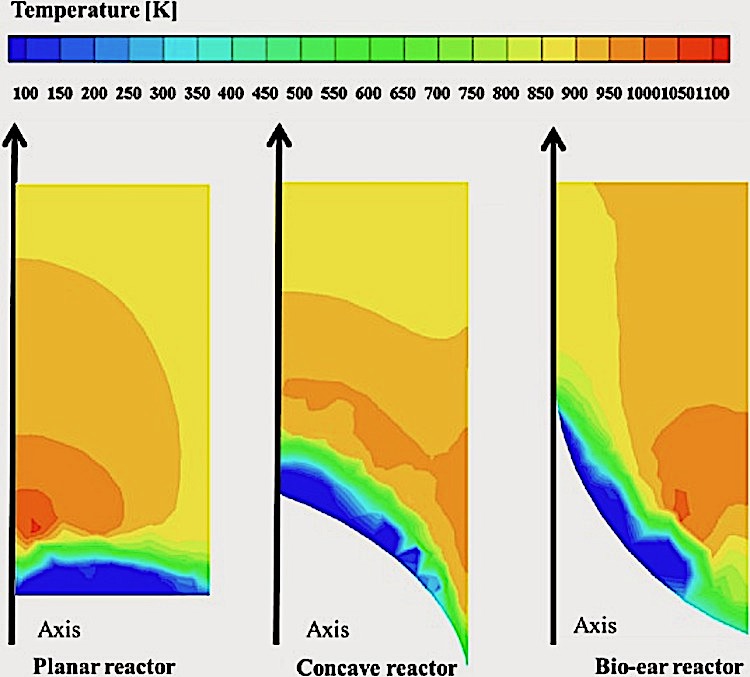
Human ear inspired solar thermochemical reactor for steam methane reforming with the consideration of minimum Gibbs free energy principle Abstract The non-uniformity temperature field of direct solar thermochemical reactors severely decreases the energy conversion efficiency of solar-to-fuel. Inspired by the physical mechanism by which the human ear can collect more sound waves, associating the similarity …
Published at Applied Energy – A novel high-efficiency solar thermochemical cycle for fuel production based on chemical-looping cycle oxygen removal
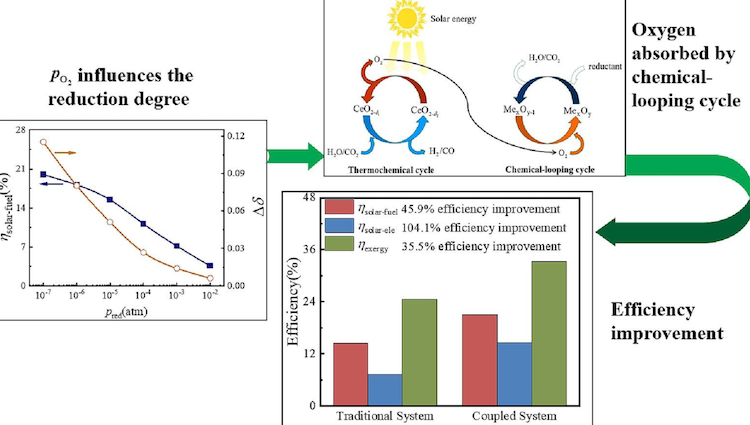
A novel high-efficiency solar thermochemical cycle for fuel production based on chemical-looping cycle oxygen removal Abstract Solar-driven two-step thermochemical cycling is a promising means to convert solar energy into storable and transportable chemical fuel, in which hydrogen or carbon monoxide is generated by continuous reduction and oxidation reactions. However, the high energy consumption of deoxygenation …
Published at Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews – Massive grid-scale energy storage for next-generation concentrated solar power: A review of the potential emerging concepts
Abstract The cost of renewable energy has significantly decreased in recent years, which marks the way towards a fully renewable and sustainable future. However, this energy transition is not possible without massive grid-scale energy storage technology since most of the renewable energies are highly variable. In areas with a high solar resource, Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) can play a …
Published at Chemical Energy Journal Advances – Experimental study on the kinetics of magnesium carbonate calcination under elevated heating rates
Abstract: This paper reports an experimental investigation into the kinetics of magnesium carbonate calcination, conducted using a broad spectrum of heating rates (0.1°C/s to 179.9°C/s) in an air environment for a thin layer bed with Biot number < 0.1. These heating rates surpass those typically employed in thermogravimetric analysers (< 1°C/s) by many orders of …
Published at Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments – Thermal desalination from rejected heat of power cycles working with CO2-based working fluids in CSP application: A focus on the MED technology
Abstract: This work analyses the integration of concentrated solar power plants based on innovative sCO2 cycles and transcritical CO2-based mixtures cycles with thermal desalination plants adopting the conventional MED technology. In these cogeneration plants, all heat rejected from the cycle is exploited by the desalination system, avoiding any parasitic electric consumption of the fans of …
Published at Chemical Engineering Transactions – Assessment of the Techno-economic Viability of the Optimal CSP Plant Technology in Egypt’s Climate
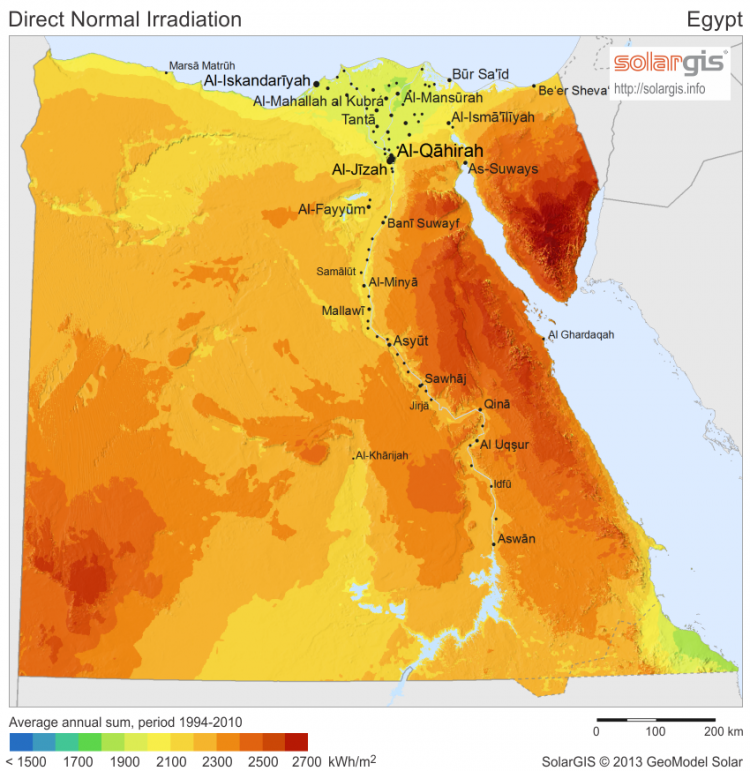
The DNI in Egyptshows a resource of 2500 along the North coast Abstract: Photovoltaic (PV) and concentrated solar power (CSP) are the two main methods for capturing solar energy. Egypt has so far focused its energy investments on solar PV technology. However, considering Egypt’s hot, dry weather throughout the year, centralized large-scale PV power generation …
Published at Chemical Engineering Science – Experimental screening of metal nitrides hydrolysis for green ammonia synthesis via solar thermochemical looping
Abstract: Ammonia is a fundamental chemical commodity for fertilizers and as a novel energy vector. Solar-driven ammonia synthesis is proposed as a sustainable alternative to the catalytic energy-intensive and CO2-emitting Haber-Bosch process. The considered thermochemical process aims to produce ammonia from nitrogen and water (N2 + 3H2O → 2NH3 + 1.5O2) via redox cycles using …
Published at Solar Energy – The cost-saving potential of next-generation particle technology CSP with steam cycles
Abstract: The cost-saving potential of next-generation concentrating solar power plants based on particle technology with steam cycles is assessed. Techno-economic models were created to optimize three systems with different steam cycles, ranging from state of the art to future development, for levelized cost of electricity and to compare them to a state-of-the-art molten salt tower …
Published at Solar Energy – Progress in research and technological advancements of commercial concentrated solar thermal power plants
Abstract: To reduce the cost of power generation from CSP technologies, over 1000 articles have been published in the last five years, and it is necessary to observe the overall research and technological advancements in this sector which is missing in the current literature. To bridge this gap, this work presents a comprehensive review on …
Published at Royal Society of Chemistry – Catalytic enhancement of production of solar thermochemical fuels: opportunities and limitations
Abstract: Solar thermochemical fuels are a promising low-carbon alternative to conventional fossil fuels, which must be swiftly phased out to mitigate the consequences of climate change. Thermochemical cycles powered by concentrating solar energy at high temperatures have demonstrated efficiency in the conversion of solar to chemical energy exceeding 5% and have been assayed in pilot …